Renault, the European leader in electric mobility, announced today the launch of Advanced Battery Storage, a stationary storage system for energy developed exclusively from EV batteries. It will have a storage capacity of at least 60 MWh, making it the biggest system of its kind ever built in Europe. The first facilities will be developed in early 2019 on three sites in France and Germany: at the Renault plants in Douai and Cléon and at a former coal-fired plant in North Rhine-Westphalia. The storage capacity will then be gradually expanded over time to contain the energy of 2,000 EV batteries. At this phase, the system will have reached – or more likely, exceed – the 60 MWh, equivalent to the daily consumption of a city of 5,000 households.
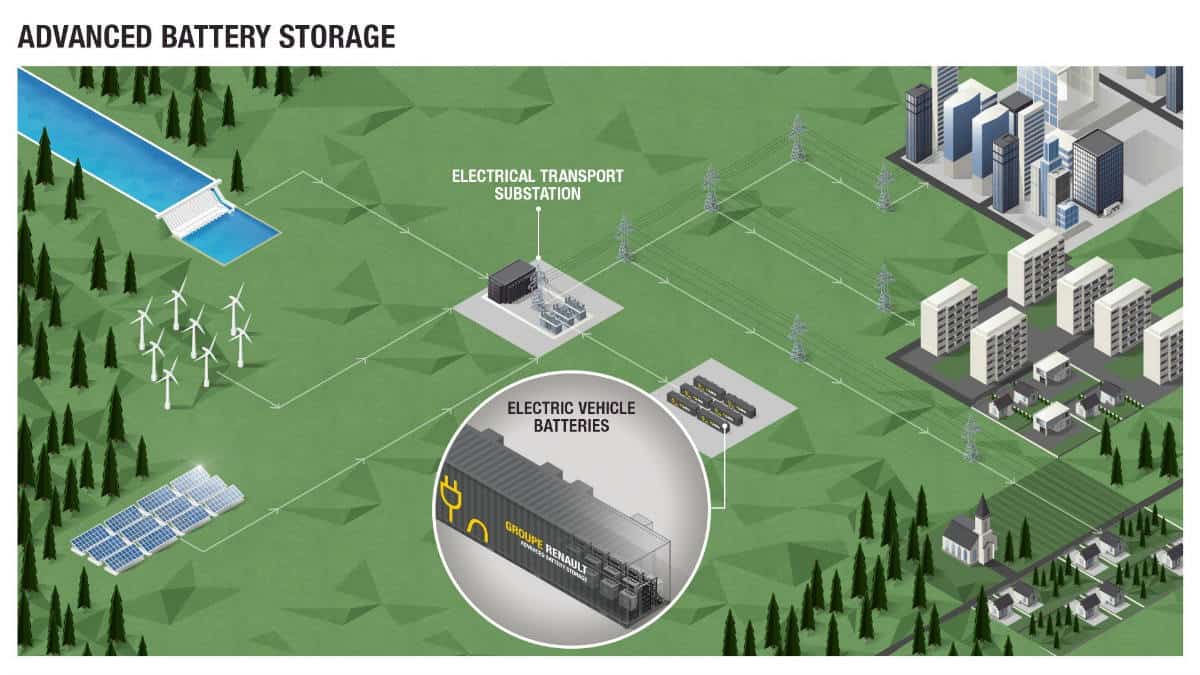
The purpose of this system is to manage the difference between electricity consumption and production at a given time, in order to increase the proportion of renewable sources in the energy mix. This means maintaining the balance between offer and demand on the electricity grid by integrating different energy sources with fluctuating production capacities. The slightest gap between consumption and production sets off disturbances that can compromise the stability of the local frequency (50 Hz). “Our stationary storage solution aims to offset these differences: it delivers its reserves to a point of imbalance in the grid at a given time to reduce the effects,” said Nicolas Schottey, Director of the Groupe Renault New Business Energy program. By helping to maintain the balance of the grid, the stationary storage system will boost the economic attractiveness of low-carbon energies.
This stationary storage system is built using EV batteries compiled in containers. The system uses second-life batteries, as well as new batteries stored for future use in
As the pioneer and leader in the field of electric mobility in Europe, Groupe Renault is extending beyond its role as a vehicle manufacturer to become a player in the smart electric and energy ecosystems, with the help of its partners. As part of the “Advanced Battery Storage” program, Groupe Renault has joined up with several players including La Banque des Territoires, the Mitsui Group, Demeter (via le Fonds de Modernisation Ecologique des Transports), and The Mobility House.
Smart charging adjusts vehicle charging to the needs of users and the electricity supply on the grid. Charging attains its maximum levels when the electricity supply exceeds demand, notably during renewable energy production peaks. Charging ceases when the demand for electricity outstrips supply by the grid, thereby optimizing the supply of local renewable energy. With reversible charging, vehicles are capable of injecting electricity into the grid during consumption peaks. In addition to being smart charged, the electric vehicles will therefore also serve as temporary energy storage units.
Once life as a power source for vehicles is over, EV batteries continue to be capable of storing a significant amount of energy. Renault is able to harness this energy in less demanding environments, notably for the purposes of stationary energy storage. By giving batteries a second lease of life, Renault is today able to cover the full spectrum of energy storage needs, from individual homes to office buildings, factories, schools and apartment blocks, and even the charging of electric vehicles.